IoT Energy Monitoring: Energy-Centered Maintenance for Sustainability
IoT Energy Monitoring: Energy-Centered Maintenance for Sustainability
- Last Updated: November 18, 2025
Nanoprecise Sci Corp
- Last Updated: November 18, 2025


The world is becoming increasingly aware of its energy consumption, from both environmental and cost perspectives. This means the ability to monitor and manage energy use across industrial operations has become critical in all industries. From manufacturing and automotive to utilities and mining, organizations are facing pressure to reduce operational costs, lower emissions, and operate more sustainably, all without compromising reliability or productivity.
One of the most powerful ways to achieve this balance is through Energy-Centered Maintenance (ECM), a maintenance strategy that builds on RCM principles, while integrating IoT sensors, AI, and edge-to-cloud analytics to identify inefficiencies, prevent failures, and drive both economic and environmental impact.
Why Energy Waste Matters
Industrial energy waste is not just a sustainability issue; it’s also a growing cost issue. Electric motors and the systems they power account for nearly two-thirds of global industrial electricity consumption.
Even small inefficiencies can have a significant impact: a slightly misaligned 100 kW pump can quietly waste thousands of dollars in electricity and generate tons of unnecessary CO₂ emissions each year!
According to Global Efficiency Intelligence, industrial electric motors account for over 70% of electricity consumption in manufacturing in the US. Improving motor efficiency alone could save up to 25% of the total industrial electricity use. With 60% of global electricity consumption tied to rotating equipment, reducing energy waste offers one of the fastest, most scalable paths to sustainability.
From Reliability-Centered Maintenance to Industrial Energy Waste Monitoring
Traditional Reliability-Centered Maintenance (RCM) focuses on equipment uptime. While effective at preventing breakdowns, it often overlooks early inefficiencies that waste energy long before failure occurs.
ECM builds on RCM by continuously assessing both equipment health and energy performance. It shifts the focus from “Is this machine running?” to “Is it running efficiently?”
ECM tracks how much energy assets consume relative to their output. When inefficiencies appear, maintenance teams can act before mechanical issues escalate and energy consumption increases further. This approach aligns operational reliability directly with sustainability performance.
IoT and Energy: Connecting Equipment to Intelligence
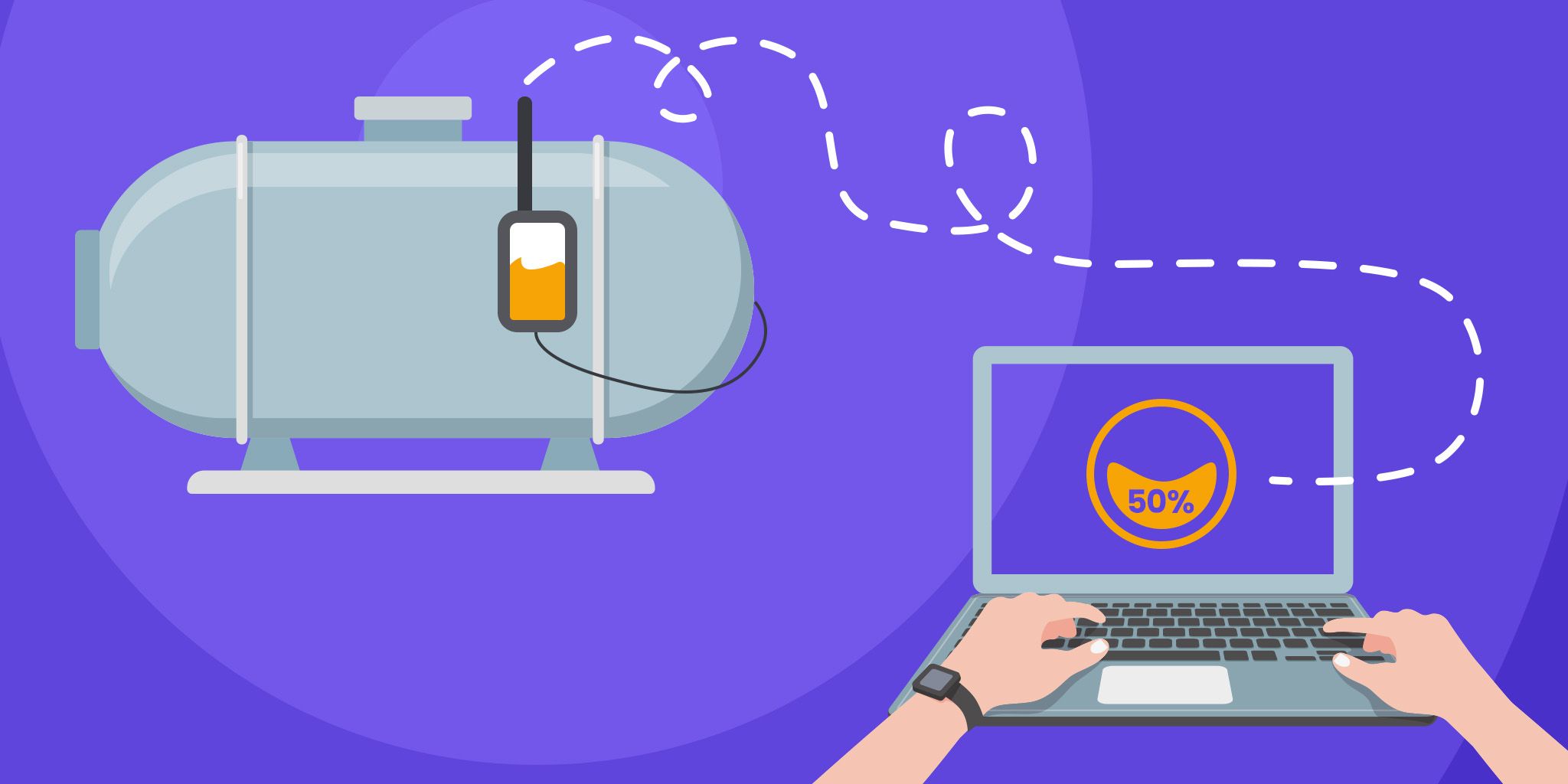
At the core of ECM are IoT-enabled sensors that attach directly to rotating industrial machinery to capture multi-variable data in real time.
Nanoprecise’s MachineDoctor sensors, for example, measure six key variables—vibration, temperature, acoustic emission, magnetic flux, humidity, and RPM. These parameters collectively create a digital fingerprint of equipment health and energy efficiency.
Here’s how IoT sensors work:
- At the edge: Sensors continuously collect and preprocess data locally, reducing transmission bandwidth and latency.
- In the cloud: The IoT device wirelessly transmits the data to the cloud, where advanced AI and machine learning algorithms analyze patterns and identify energy or performance anomalies.
- For the user: Actionable insights are visualized through dashboards or automated alerts, empowering maintenance teams to intervene early, and before minor deviations become costly failures or sources of energy waste.
This closed-loop IoT ecosystem (from edge to cloud) creates a seamless, automated way to detect inefficiencies, reduce downtime, and support measurable sustainability outcomes.
Predictive Maintenance Meets Sustainability
While ECM sounds similar to Predictive Maintenance (PdM), it differs in that PdM systems rely mainly on mechanical, reliability-centered machine signals, such as vibration or temperature, and identify faults only after inefficiencies are already occurring.
Whereas ECM creates strong industrial reliability AND energy monitoring systems that detect changes in power consumption before other mechanical symptoms emerge. This is because when machines operate under stress (due to imbalance, misalignment, or wear) they consume more energy to compensate.
By identifying these subtle spikes early, ECM gives maintenance teams valuable lead time to proactively address problems, cutting both downtime and carbon emissions.
The IoT sensors used as part of ECM, continuously analyze energy consumption as well as subtle changes in vibration, and temperature—patterns often invisible to traditional PdM. These insights empower teams to fine-tune operations, reduce inefficiencies, and directly measure reductions in energy consumption and CO₂ emissions.
This energy-first approach turns maintenance into a strategic sustainability tool. It allows teams to:
- Plan maintenance on their own schedule instead of reacting to failures.
- Reduce overtime, emergencies, and energy waste.
- Focus on long-term reliability and sustainability initiatives rather than daily firefighting.
A Real-World example
A leading chemical manufacturer needed better visibility into equipment health.
Through continuous IoT data analysis, the system detected abnormal vibration levels on two refrigeration pump motors early on. The fault was also causing the motors to consume 20% more energy than usual.
This early detection gave the team enough time to intervene, preventing a $50,000 motor replacement, avoiding $9,422 in annual energy costs (for just one motor), and reducing CO₂ emissions by 17,071 kg.
Measurable Impact: Increasing Industrial Sustainability and Safety
Energy-Centered Maintenance delivers benefits across multiple dimensions:
- Energy Savings: Industrial facilities typically achieve 5–15% reductions in energy consumption, while building systems that can see up to 20% savings.
- Carbon Reduction: Lower energy waste means direct GHG emission reductions, aligning operations with corporate ESG and net-zero goals.
- Operational Efficiency: Detecting issues earlier improves reliability, extends asset life, and reduces maintenance costs.
- Workplace Safety: Fewer emergency shutdowns and reactive interventions lead to safer working environments.
By merging reliability and energy intelligence, ECM helps organizations simultaneously enhance uptime, reduce costs, and improve sustainability performance.
Energy Centered Maintenance is The Future of Sustainable Maintenance
As industries race toward net-zero and energy efficiency targets, the integration of IoT sensors, AI-driven analytics, and Energy-Centered Maintenance represents the future of operational excellence.
By combining IoT devices, edge intelligence, cloud analytics, and machine learning, organizations can transform maintenance from a reactive function into a proactive sustainability strategy—driving measurable impact across cost, reliability, and environmental performance.
The Most Comprehensive IoT Newsletter for Enterprises
Showcasing the highest-quality content, resources, news, and insights from the world of the Internet of Things. Subscribe to remain informed and up-to-date.
New Podcast Episode

IoT in 2026: Trends and Predictions
Related Articles